30th April 2025, Gaurav Kumar Singh
How Avni’s EMI Increased – A Real-Life Example
Avni had a dream – to buy her own home. She finally made it happen and bought a house worth ₹1 crore. Out of this, she took a home loan of ₹70 lakhs from her local bank for 20 years at an interest rate of 7% per year. The remaining ₹30 lakhs came from her savings and help from her parents.

Her monthly EMI (the amount she had to pay the bank every month) was ₹54,271. But after just 6 months, her bank informed her that her EMI would now increase to ₹56,392 because the interest rate on her loan had gone up to 7.5%. Why? Because RBI had increased interest rates.
This shows how changes in interest rates by the RBI can impact your finances directly.
What is Monetary Policy?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is like the money manager of our country. It decides the monetary policy, which simply means how the RBI manages interest rates and money supply in the economy.
A special group called the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) – headed by the RBI Governor – meets every two months to review the economy.
They look at things like:
• Inflation (rise in prices of goods and services)
• Economic growth
• Rainfall predictions (important for farming)
• Global events and interest rates in other countries
• Commodity prices (like fuel, metals, food grains)
Based on all this, they decide whether to increase, decrease, or keep the interest rates the same.
Understanding Repo Rate and Why It Matters
One of the main tools used by RBI is the Repo Rate.
This is the rate at which RBI lends money to banks.
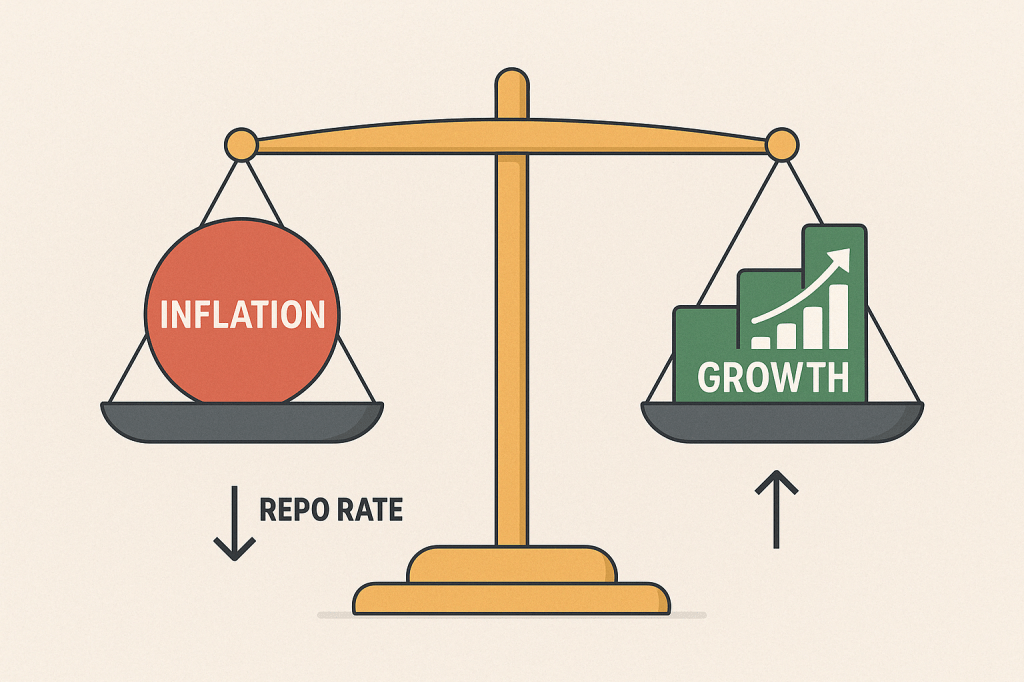
If RBI increases the Repo Rate:
• Banks have to pay more to borrow money from RBI.
• Banks then charge more from customers for loans.
• So, loan EMIs for home, car, or education loans go up.
• Result: People like Avni have to pay more every month.
If RBI reduces the Repo Rate:
• Loans become cheaper.
• People can borrow more easily.
• More money is spent in the market.
• This boosts economic growth.
But it can also lead to higher inflation if too much money is floating around.
Why Does RBI Change Interest Rates?
If prices of everyday goods are rising fast (high inflation), RBI might increase interest rates. This makes borrowing expensive, so people spend less. That helps bring prices down.
But if the economy is growing slowly and people are not spending enough, RBI might cut interest rates. This encourages borrowing and spending.
So, it’s all about maintaining a balance between:
• Inflation (keeping prices in check)
• Growth (ensuring the economy keeps moving forward)
How It Affects You and Me
Let’s go back to Avni. Because the Repo Rate increased, her home loan EMI also increased. That meant she had less money left for shopping, outings, or travel. The same happens across the country – when millions of people pay higher EMIs, they cut back on spending.
Even companies feel the impact. If interest rates are high, businesses avoid taking new loans for expansion. They may delay buying new machinery, hiring staff, or opening new offices. This slows down job creation and growth.
So, the entire economy is affected by this one decision of RBI.
RBI’s Other Tool – Liquidity Management
RBI can also control the amount of money in the system. Here’s how:
• If there’s too much money and inflation is rising, RBI can sell bonds. This pulls out excess money from the system.
• If the economy needs a boost, RBI can buy bonds and pump more money into the market.
This is called liquidity management – another way to keep inflation and growth balanced.
Interest Rates Move in Cycles
Interest rates don’t stay the same forever. They follow a cycle:
• First they go up
• Then they come down
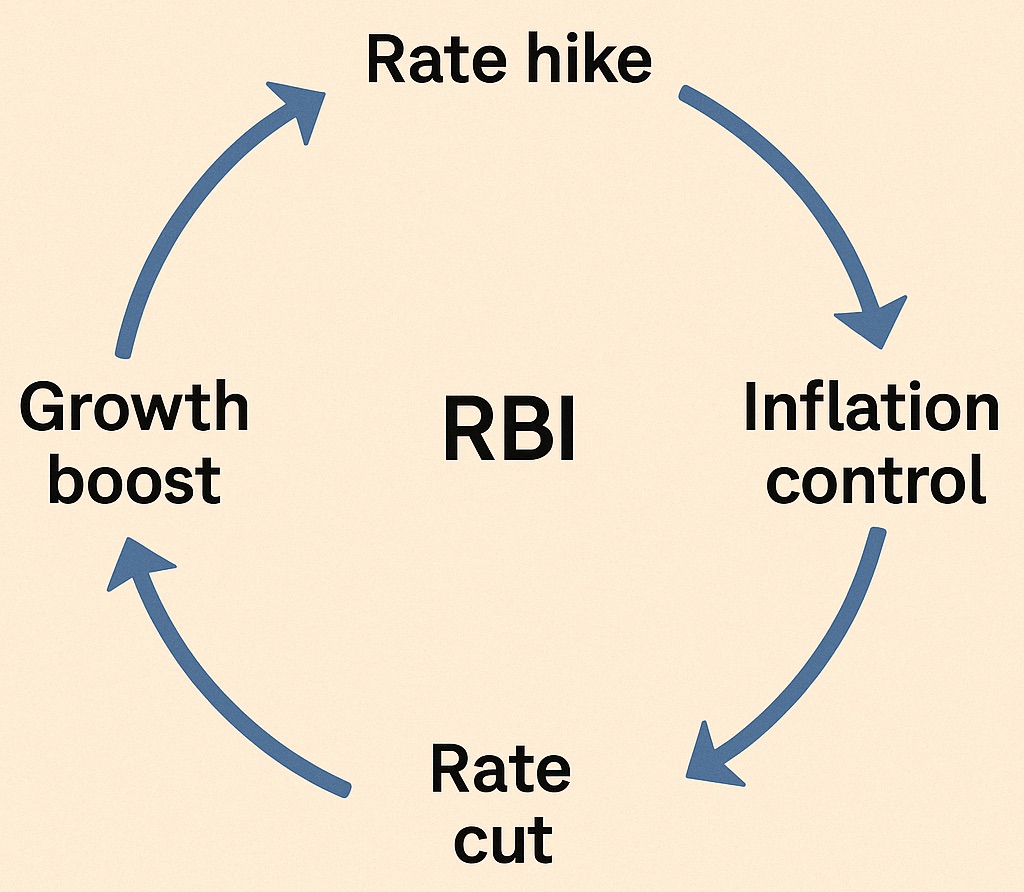
RBI has a target to keep inflation between 2% and 6%. If inflation is low and under control, RBI can cut rates to support growth.
Monetary Policy vs Fiscal Policy
Don’t confuse monetary policy with fiscal policy:
• Monetary Policy is controlled by RBI (interest rates, liquidity).
• Fiscal Policy is controlled by the Government (taxes, government spending).
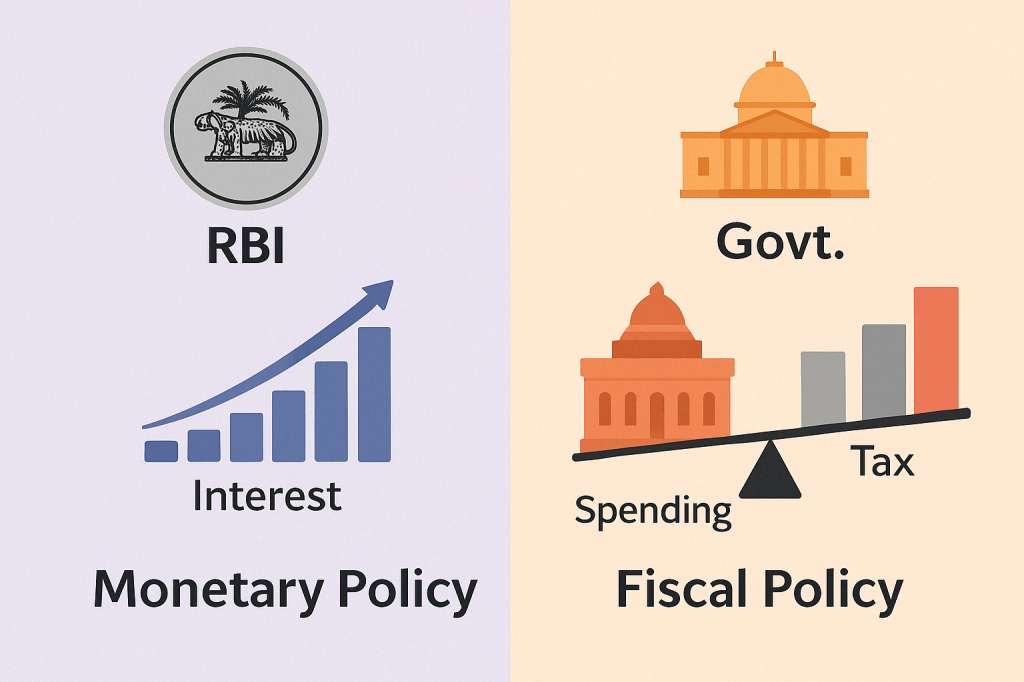
While RBI can make loans cheaper, the government can reduce income or corporate taxes to put more money in your pocket.
In a Nutshell
Monetary policy is a powerful tool that affects all of us – whether you are a salaried person, student, business owner, or investor.
So the next time your EMI goes up, or you hear RBI is changing the Repo Rate, you’ll know why! It’s not just about numbers – it’s about the economy, inflation, savings, spending, and your financial wellbeing.

If you found this article valuable, please don’t forget to Like and Subscribe to my blog for more expert insights and updates.


Leave a comment