21st April 2025, Gaurav Kumar Singh
Have you ever wondered how the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) controls inflation or manages money in the economy? One important tool it uses is called the Repo Rate. Don’t worry if it sounds complicated – in this article, we’ll break it down into simple words so anyone can understand!
What is Repo Rate?
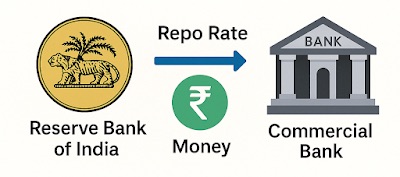
Repo Rate stands for Repurchase Rate. It is the interest rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks like SBI, HDFC, or ICICI for a short period.
In simple terms:
When banks need money, they go to RBI and borrow it. The interest they pay on this borrowing is called the Repo Rate.
Why is it called ‘Repo’?
The word “Repo” comes from Repurchase Agreement. Banks sell government securities to RBI with a promise to buy them back later. So, it’s not just a loan – it’s like a short-term sale with a promise to repurchase.
Why is Repo Rate Important?
Repo Rate affects everything from your home loan EMIs to car loan interest and even prices in the market.
Here’s how:
1. Controlling Inflation
- When inflation is high, the RBI increases the repo rate.
- This makes borrowing expensive for banks, which means loans become expensive for people.
- People borrow and spend less, and this helps reduce inflation.
2. Boosting Growth
- When the economy is slow, the RBI lowers the repo rate.
- Loans become cheaper, and people and businesses borrow more.
- This increases spending and boosts the economy.
How Does It Affect You?
Here’s a simple example:
Imagine you want to take a home loan. If the RBI increases the repo rate, your bank may also increase its lending rate. That means your EMIs will go up!
If the RBI reduces the repo rate, your EMIs may reduce, making loans cheaper and saving you money.
Current Repo Rate
The repo rate is not fixed forever. RBI reviews it every two months during its Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meetings.
You can check the latest repo rate on the RBI’s official website or financial news platforms.
Quick Summary
- Repo Rate = Interest rate at which the RBI lends money to banks.
- Used to control inflation and economic growth.
- Affects your loans, EMI’s, and interest rates.
- Changed regularly by the RBI depending on the economic situation.

If you found this article valuable, please don’t forget to Like and Subscribe to my blog for more expert insights and updates.